
Veterinary Resources

Purina Equine Veterinary Manual
Valuable Resources for Helping your Equine Clients
It is very important to us at Purina that we can partner with local veterinarians across Canada to ensure that our customers are utilizing the full potential of our equine products in order to meet the specific nutritional needs of their horse. Included in this manual you will find many valuable resources that will assist you when helping your clients decide the best nutritional and management recommendations for their specific situation.
-

Malignant Hyperthermia
Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a genetic disorder (autosomal dominant trait) and may occur in conjunction with type 1 PSSM.
Read More -

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) or Heaves
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) or “heaves” is a respiratory disease that can be the result of an allergic response.
Read More -

Deficiencies in Horses
The main cause of deficiency is malnutrition or underfeeding. The horse is simply not getting enough or not at all of one or more nutrients, be it calories, protein, minerals or vitamins.
Read More -
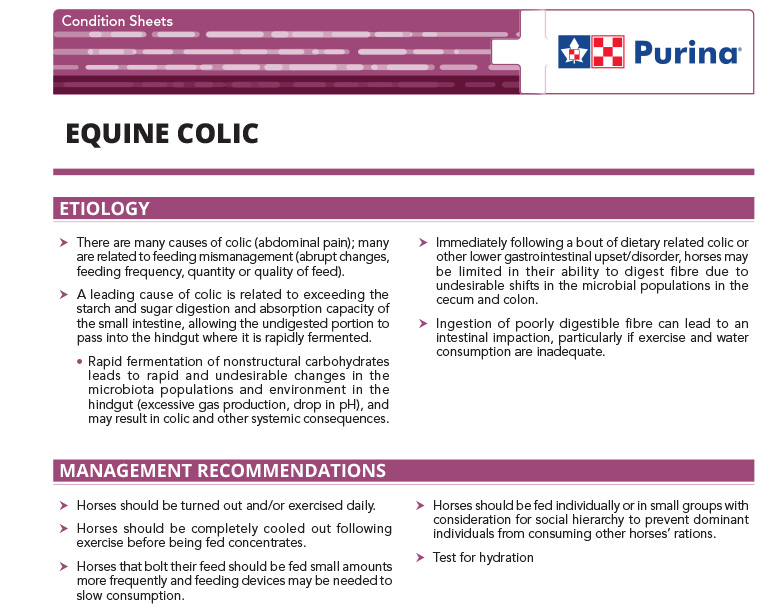
Equine Colic
There are many causes of colic (abdominal pain); many are related to feeding mismanagement.
Read More
-

Equine Cushing’s Disease or Pituitary Pars Intermedia Dysfunction (PPID)
Etiology of PPID includes hypertrophy, hyperplasia and adenoma formation of the pars intermedia lobe of the pituitary gland, which results in excessive adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion and subsequent increased secretion of cortisol from adrenal glands.
Read More -
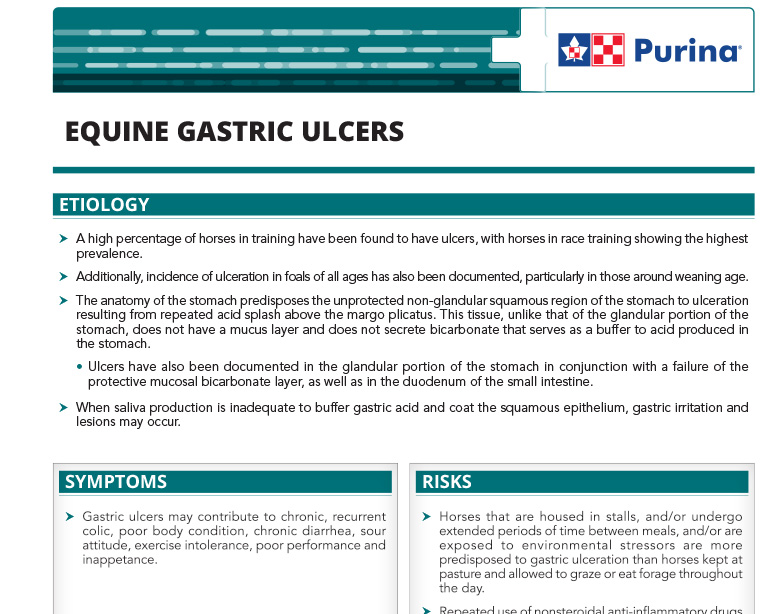
Equine Gastric Ulcers
A high percentage of horses in training have been found to have ulcers, with horses in race training showing the highest prevalence.
Read More -

Equine Insulin Resistance
IR can be described as a reduced sensitivity or failure of cells to respond properly to physiologically “normal” levels of insulin.
Read More -
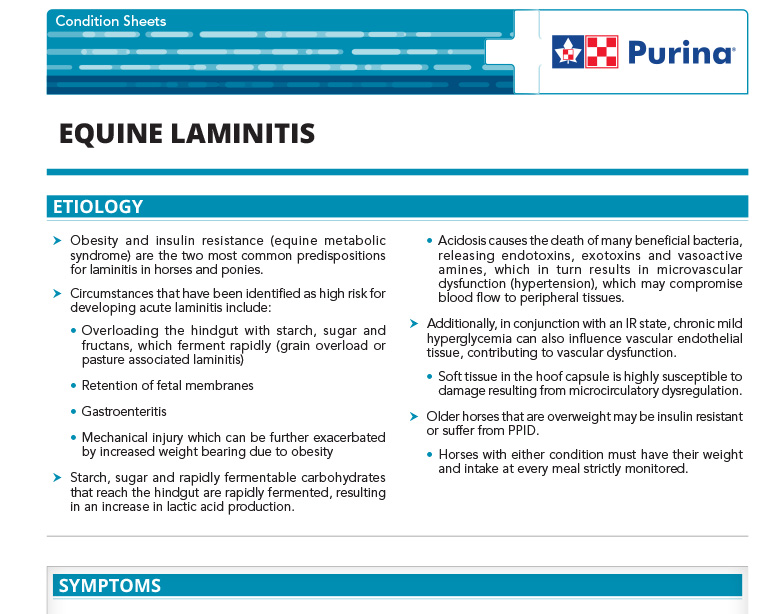
Equine Laminitis
Obesity and insulin resistance (equine metabolic syndrome) are the two most common predispositions for laminitis in horses and ponies.
Read More
-
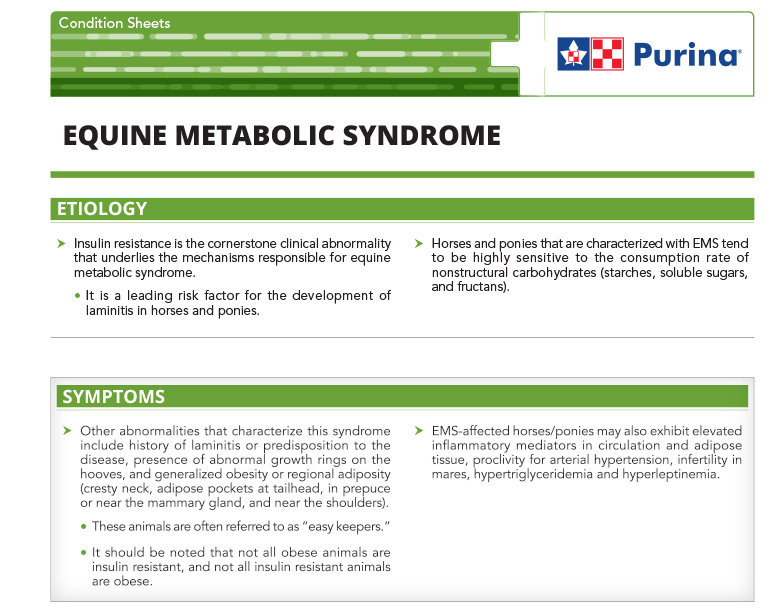
Equine Metabolic Syndrome
Insulin resistance is the cornerstone clinical abnormality that underlies the mechanisms responsible for equine metabolic syndrome.
Read More -
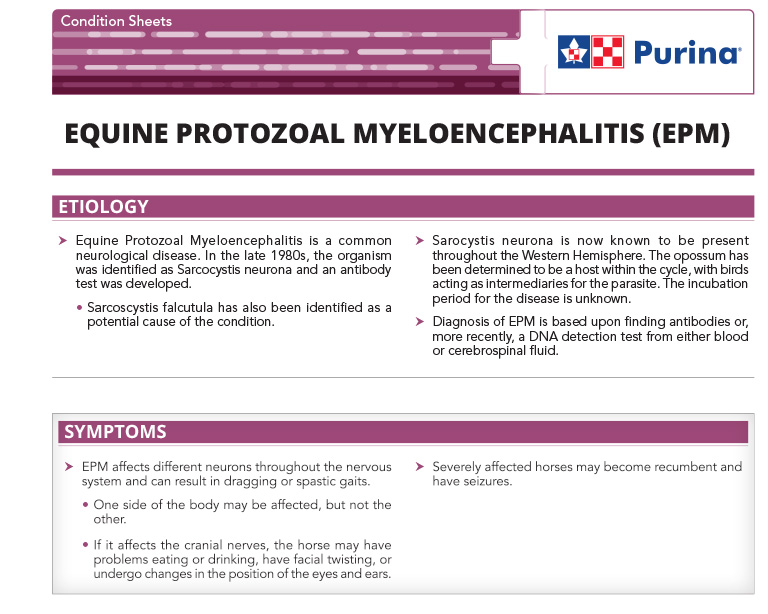
Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis (EPM)
Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis is a common neurological disease.
Read More -

Excitable Behaviour in Horses
Horses that are overfed and underworked, particularly when stalled, may exhibit excitable behaviour.
Read More -

Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HYPP) is an inherited (autosomal dominant trait) muscle disease.
Read More
-
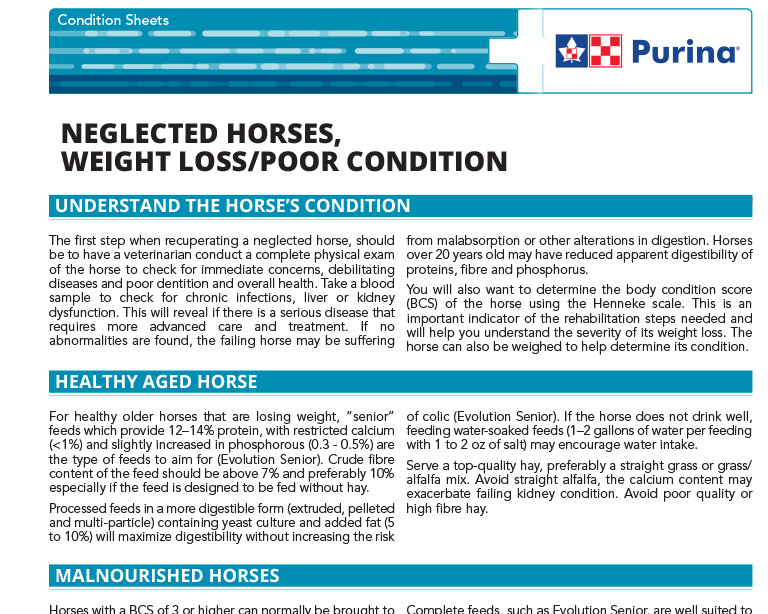
Neglected Horses, Weight Loss/Poor Condition
The first step when recuperating a neglected horse, should be to have a veterinarian conduct a complete physical exam of the horse to check for immediate concerns, debilitating diseases and poor dentition and overall health.
Read More -

Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD) or Developmental Orthopedic Disease (DOD)
Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a condition in young, rapidly growing horses that is classified as part of a group of conditions called Developmental Orthopedic Disease (DOD).
Read More -

Overweight Horses
Obesity in horses can lead to laminitis, colic, insulin resistance, overheating and numerous other health conditions.
Read More -
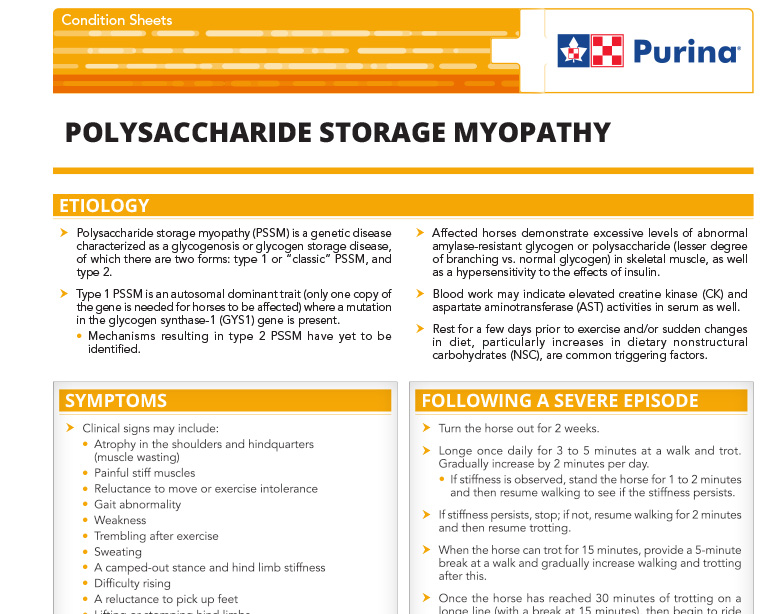
Polysaccharide Storage Myopathy
Polysaccharide storage myopathy (PSSM) is a genetic disease characterized as a glycogenosis or glycogen storage disease, of which there are two forms: type 1 or “classic” PSSM, and type 2.
Read More
-

Recurrent Exertional Rhabdomyolysis
Recurrent exertional rhabdomyolysis (RER) is a genetic disease seen in several breeds, namely Thoroughbreds, Arabians, and Standardbreds, and tends to be more common in high-strung or nervous fillies.
Read More -

Renal and Hepatic Disease
Renal disease is not very common in horses. Hepatic disease is slightly more common.
Read More -

Underweight Horses
Horses that are losing weight during competition are not receiving enough calories, or they may be overly stressed or unsound.
Read More
Explore Equine Products
-
 Purina®
Purina®
Digestive Balance
13.0% Crude Protein (min.)2.0% Crude Fat (min.)17.0% Crude Fibre (max.)Digestive Balance is a specialized supplement designed to help horses aged six months and over maintain optimal digestive health.Learn More -
 Purina® SuperFibra
Purina® SuperFibra
Classic
12.5% Protein2.0% Fat25.0% FibreFortified feed for horsesLearn More -
 Purina® Equilibrium
Purina® Equilibrium
Equilizer
12.0% Protein4.0% Fat15.0% FibreVitamins and minerals for horsesLearn More
Read More Articles
-

Understanding Selenium
Selenium is a trace mineral (or micromineral), which means it is essential to bodily functions but in very small quantities as opposed to macrominerals such as calcium or magnesium which must be provided in larger amounts.
Read Article -

Nutrition Myths
There are many persistent myths in the horse world. People do all kinds of things by habit or by relying on advice from friends, such as a neighbour for whom a certain solution worked, or a coach who hasn’t necessarily seen the specific horse.
Read Article -

Changes in your Horse’s Diet
Whatever the reason, switching your horse to a new feed is a change that requires care and know-how.
Read Article -

Healthy Hooves Need Good Nutrition
No hoof, no horse! Horse people understand perfectly well this old adage! But what are a horse’s real nutritional needs for healthy feet, and when should adding a hoof supplement be considered?
Read Article
